Altmetrics
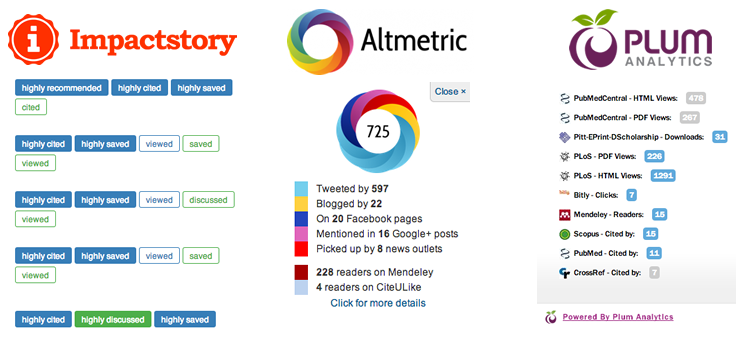
Long considered primary way to measure the impact of research publications, the impact factor is being both challenged and supplemented by the use of altmetrics. Faculty members who want to explore altmetrics can work with LTS staff to use web-based tools to measure the impact their research and scholarship beyond simple citation tracking.
What are altmetrics?
With the explosion of “big data,” we can find out more about articles and other research output, and we can do it on a faster timeline than in the past. Altmetrics have the potential to do the following: "provide a broader, more diverse view of the impact of any piece of scholarship, to reflect the impact of the article itself, not its publication venue, to track impact outside the academy, to track the impact of influential but uncited work, and to track track impact from sources that aren't peer-reviewed." (source: http://altmetrics.org/manifesto)
Altmetrics services generally track impact by looking at and quantifying:
- usage - views, downloads, holdings, document delivery, ILL
- captures - favorites, bookmarks, saves, readers
- mentions - blog posts, Wikipedia articles, news stories, comments, reviews
- social media - tweets, +1s, likes, shares, ratings
- citation - Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar, PubMed, patents
Depending on the service, we can identify altmetrics for a large range of scholarly objects, including articles, blog posts, book chapters, books, cases, clinical trials, conference papers, datasets, figures, grants, interviews, letters, media, patents, posters, presentations, source code, theses and dissertations, videos, and web pages.
LTS Contact: Megan Brooks
Keywords: altmetrics, citation, measurement, data
Thumbnail image used under a Creative Commons license.
